Note
This page was generated from circuit-examples//A.Qubits//10-Transmon_floating_teeth.ipynb.
Single Transmon - Floating with teeth#
We’ll be creating a 2D design and adding a single transmon qcomponent with teeth.
Create a standard pocket transmon qubit with teeth for a ground plane, with two pads connected by a junction.
[1]:
# So, let us dive right in. For convenience, let's begin by enabling
# automatic reloading of modules when they change.
%load_ext autoreload
%autoreload 2
[2]:
import qiskit_metal as metal
from qiskit_metal import designs, draw
from qiskit_metal import MetalGUI, Dict, open_docs
[3]:
# Each time you create a new quantum circuit design,
# you start by instantiating a QDesign class.
# The design class `DesignPlanar` is best for 2D circuit designs.
design = designs.DesignPlanar()
[4]:
#Launch Qiskit Metal GUI to interactively view, edit, and simulate QDesign: Metal GUI
gui = MetalGUI(design)
[5]:
# To force overwrite a QComponent with an existing name.
# This is useful when re-running cells in a notebook.
design.overwrite_enabled = True
A transmon qubit with teeth#
You can create a ready-made transmon qubit with teeth from the QComponent Library, qiskit_metal.qlibrary.qubits. transmon_pocket_teeth.py is the file containing our qubit so transmon_pocket_teeth is the module we import. The TransmonPocketTeeth class is our transmon qubit. Like all quantum components, TransmonPocketTeeth inherits from QComponent.
Connector lines can be added using the connection_pads dictionary. Each connector pad has a name and a list of default properties.
[6]:
from qiskit_metal.qlibrary.qubits.transmon_pocket_teeth import TransmonPocketTeeth
# Be aware of the default_options that can be overridden by user.
TransmonPocketTeeth.get_template_options(design)
[6]:
{'pos_x': '0um',
'pos_y': '0um',
'connection_pads': {},
'_default_connection_pads': {'pad_gap': '15um',
'pad_width': '20um',
'pad_height': '150um',
'pad_cpw_shift': '0um',
'pad_cpw_extent': '25um',
'cpw_width': '10um',
'cpw_gap': '6um',
'cpw_extend': '100um',
'pocket_extent': '5um',
'pocket_rise': '0um',
'loc_W': '+1',
'loc_H': '+1'},
'chip': 'main',
'pad_gap': '30um',
'inductor_width': '20um',
'pad_width': '400um',
'pad_height': '90um',
'pocket_width': '650um',
'pocket_height': '650um',
'coupled_pad_height': '150um',
'coupled_pad_width': '20um',
'coupled_pad_gap': '50um',
'orientation': '0',
'hfss_wire_bonds': False,
'q3d_wire_bonds': False,
'hfss_inductance': '10nH',
'hfss_capacitance': 0,
'hfss_resistance': 0,
'hfss_mesh_kw_jj': 7e-06,
'q3d_inductance': '10nH',
'q3d_capacitance': 0,
'q3d_resistance': 0,
'q3d_mesh_kw_jj': 7e-06,
'gds_cell_name': 'my_other_junction'}
[7]:
transmon_options = dict(
pos_x = '1mm',
pos_y = '2mm',
orientation = '90',
connection_pads=dict(
readout = dict(loc_W=0, loc_H=+1),
),
gds_cell_name='FakeJunction_01',
)
# Create a new Transmon Pocket object with name 'Q1'
q1 = TransmonPocketTeeth(design, 'Q1', options=transmon_options)
gui.rebuild() # rebuild the design and plot
gui.autoscale() # resize GUI to see QComponent
gui.zoom_on_components(['Q1']) #Can also gui.zoom_on_components([q1.name])
Let’s see what the Q1 object looks like
[8]:
q1 #print Q1 information
[8]:
name: Q1
class: TransmonPocketTeeth
options:
'pos_x' : '1mm',
'pos_y' : '2mm',
'connection_pads' : {
'readout' : {
'pad_gap' : '15um',
'pad_width' : '20um',
'pad_height' : '150um',
'pad_cpw_shift' : '0um',
'pad_cpw_extent' : '25um',
'cpw_width' : '10um',
'cpw_gap' : '6um',
'cpw_extend' : '100um',
'pocket_extent' : '5um',
'pocket_rise' : '0um',
'loc_W' : 0,
'loc_H' : 1,
},
},
'chip' : 'main',
'pad_gap' : '30um',
'inductor_width' : '20um',
'pad_width' : '400um',
'pad_height' : '90um',
'pocket_width' : '650um',
'pocket_height' : '650um',
'coupled_pad_height': '150um',
'coupled_pad_width' : '20um',
'coupled_pad_gap' : '50um',
'orientation' : '90',
'hfss_wire_bonds' : False,
'q3d_wire_bonds' : False,
'hfss_inductance' : '10nH',
'hfss_capacitance' : 0,
'hfss_resistance' : 0,
'hfss_mesh_kw_jj' : 7e-06,
'q3d_inductance' : '10nH',
'q3d_capacitance' : 0,
'q3d_resistance' : 0,
'q3d_mesh_kw_jj' : 7e-06,
'gds_cell_name' : 'FakeJunction_01',
module: qiskit_metal.qlibrary.qubits.transmon_pocket_teeth
id: 1
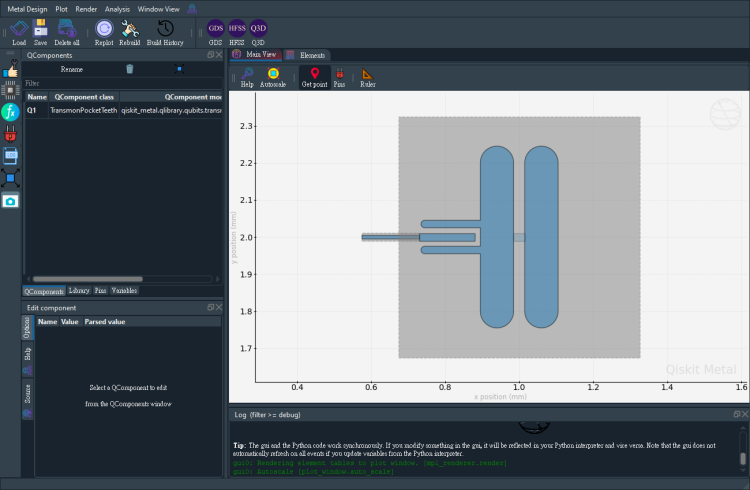
Save screenshot as a .png formatted file.
[9]:
gui.screenshot()
[10]:
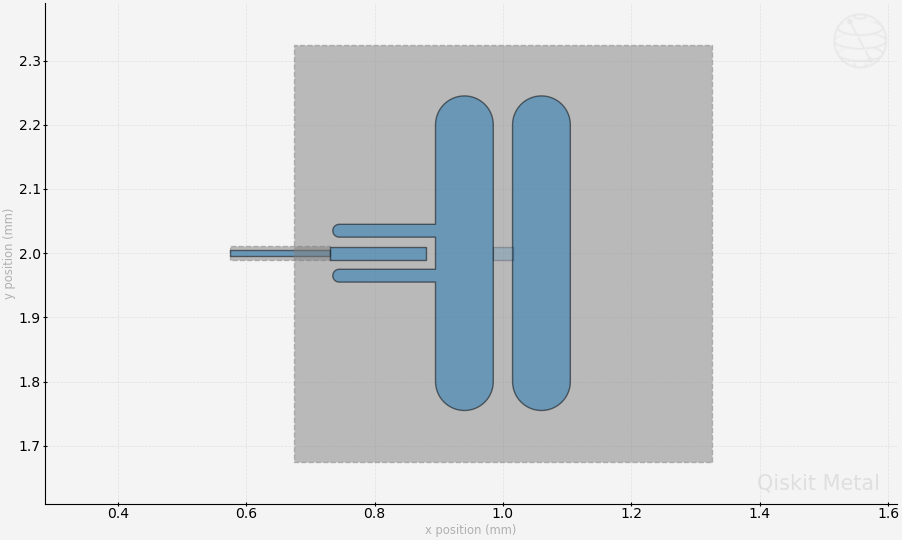
# Screenshot the canvas only as a .png formatted file.
gui.figure.savefig('shot.png')
from IPython.display import Image, display
_disp_ops = dict(width=500)
display(Image('shot.png', **_disp_ops))
Closing the Qiskit Metal GUI#
[11]:
gui.main_window.close()
[11]:
True
[ ]:
For more information, review the Introduction to Quantum Computing and Quantum Hardware lectures below
|
Lecture Video | Lecture Notes | Lab |
|
Lecture Video | Lecture Notes | Lab |
|
Lecture Video | Lecture Notes | Lab |
|
Lecture Video | Lecture Notes | Lab |
|
Lecture Video | Lecture Notes | Lab |
|
Lecture Video | Lecture Notes | Lab |